Last update: May 5, 2025, Contributors: Piyumal Demotte, Minh Bui, Rob Lanfear
Phylogenetic Dating
Bayesian dating with MCMCtree
From IQ-TREE version 3.0.1 onwards, we provide the functionality in IQ-TREE to infer time trees using Bayesian MCMCtree method.
If you use this feature, please cite:
P. Demotte, M. Panchaksaram, H. Kumarasinghe, N. Ly-Trong, M. dos Reis, and B.Q. Minh (2025) IQ2MC: A New Framework to Infer Phylogenetic Time Trees Using IQ-TREE 3 and MCMCTree with Mixture Models. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2CD2X
IQ2MC workflow for time tree inference
The IQ2MC workflow has three steps that integrate IQ-TREE and MCMCtree. The final output is a time-estimated phylogeny starting from a multiple-sequence alignment as displayed in the following figure.
Step1: Given an input multiple sequence alignment, IQ-TREE will infer the maximum likelihood tree using the IQ-TREE tree search algorithm. Note that, the tree estimated here should be a rooted tree or you need to manually root the tree as MCMCtree only accepts rooted trees for phylogenetic dating. In this step, IQ-TREE also estimates the best-fitted substitution model for the data if you do not specify the model. This step is optional if you provide a rooted tree, the MSA, and the substitution model for step 2.step2: For fast approximate likelihood dating, MCMC requires the gradients and the Hessian/Hessians of the branch lengths calculated at maximum likelihood estimates. Given the rooted tree with fossil/tip calibrations, the substitution model, and the MSA, IQ-TREE generates the Hessian file containing the gradients and the Hessian/Hessian and all required files to run MCMCtree for dating. If the rooted tree provided for this step does not include fossil/tip calibrations, users need to calibrate the tree with commonly used tree editing tools such as FigTree or iTOL before step 3.step3: Now, you can directly run MCMCtree from the IQ-TREE output of step 2 and infer the time tree.
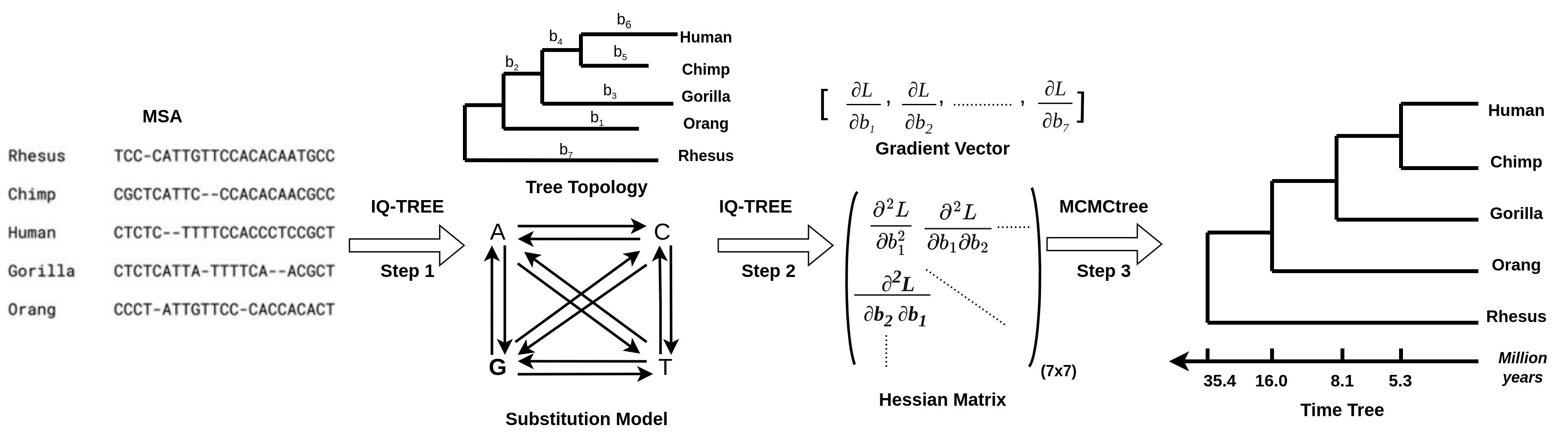
Estimating the gradients and the Hessian for MCMCtree dating
To obtain the Hessian file for MCMCtree approximate likelihood dating, you need to perform step 2 in the workflow. For this step, IQ-TREE expects a rooted tree file, the substitution model, and the multiple sequence alignment. When --dating mcmctree option is used as below, IQ-TREE performs the gradients and the Hessian calculation and generates the Hessian file. This Hessian file is compatible with MCMCtree and you can use it as an input to MCMCtree for approximate likelihood dating.
If the alignment file is called example.phy and the rooted tree file is called example_tree.nwk,
iqtree3 -s example.phy -m GTR+G4 -te example_tree.nwk --dating mcmctree --prefix example
Note that, Here we generate the Hessian file for a fixed rooted tree. You can directly input the rooted tree which already contains fossil/tip calibration information added using tree editing tools such as FigTree. When using the above command, IQ-TREE generates the following files which can be used to run MCMCtree for phylogenetic dating.
example.mcmctree.hessian: the hessian file which contains the gradients vector and the Hessian for approximate likelihood dating.example.rooted.nwk: the rooted tree file which is compatible with the Hessian file. It is necessary to use this tree file with MCMCtree for dating as the Hessian is calculated with respect to the ordering of taxa of this tree file.example.mcmctree.ctl: the control file that can be used directly to run MCMCtree from IQ-TREE output of step 2.example.dummy.aln: It is not necessary to use the alignment with MCMCtree under approximate likelihood dating. However, in the current format MCMCtree requires an alignment, and you can simply use this dummy alignment file as the input to MCMCtree to save compute.
You can specify more parameters in the workflow to generate the control file accurately for the analysis with IQ-TREE.
iqtree3 -s example.phy -m GTR+G4 -te example_tree.nwk --dating mcmctree --mcmc-iter 20000,200,50000 --mcmc-bds 1,1,0.5 --mcmc-clock IND
--mcmc-iter burnin,samplefreq,nsample: use to set number of burin samples, sample frequency, and number of MCMC samples in the control file. In the above example, burnin =20000, samplefreq = 200, and nsample = 50000--mcmc-bds birth-rate,death-rate,sampling-fraction: use to set the parameters for birth-death prior in MCMCtree. In the above example, birth-rate=1, death-rate=1, and sampling-fraction=0.5--mcmc-clock <EQUAL|IND|CORR>: use to set clock model for MCMCtree. Currently supported clocks models are EQUAL: global clock with equal rates, IND: independent rates model with independent rates across lineages and CORR: correlated clock model with auto-correlated rates across the lineages.
Using partitions and mixture models for approximate likelihood dating
IQ-TREE supports three partition models for approximate likelihood dating. Under the Edge-unlinked (EUL) model (-Q option), IQ-TREE generates the Hessian file which contains separate gradients and Hessian for each partition. For the Edge-linked (EL) partition model (-p option), the Hessian file contains only one gradient vector and a Hessian as branches are shared across partitions. See Complex Models for how to specify partition and mixture models. If your partition file is called example.nex:
# -Q option is to specify egde-unlinked partition model
iqtree3 -s example.phy -Q example.nex -m GTR+G4 -te example_tree.nwk --dating mcmctree
IQ-TREE also supports mixture models for the Hessian file generation. You can simply specify DNA or Amino Acid Mixture model as following,
iqtree3 -s example.phy -m "MIX{GTR,HKY}+G4" -te example_tree.nwk –-dating mcmctree
(Or you can also invoke MixtureFinder with -m MIX+MFP to determine mixture models automatically).
If you need to use an Amino Acid profile mixture model such as C60 model,
iqtree3 -s example_aa.phy -m LG+G4+C60 -te example_aa_tree.nwk –-dating mcmctree
How to run MCMCtree
You need to download a modified version of MCMCTree from https://github.com/iqtree/paml. This version has some changes to make the workflow more convenient. You can then directly run MCMCtree from the control file generated by IQ-TREE in step 2. The command to run MCMCtree with the control file is:
mcmctree example.mcmctree.ctl
The control file generated by IQ-TREE has the following format. You can edit the control file before running mcmctree as necessary. For example, you can increase burnin and sample frequency for MCMC convergence.
seed = -1 * The computer’s current time is used when seed < 0.
seqfile = example.dummy.phy * A dummy alignment only allow to run MCMCtree
treefile = example.rooted.nwk * Rooted newick tree with annotated fossil/tip dates
mcmcfile = example.mcmctree.log * MCMC log of parameters that can be examined in Tracer
outfile = example.mcmctree.out * Output of the summarized results of MCMCtree
ckpfile = example..mcmctree.ckp * Checkpoint file of MCMCtree
hessianfile = example.mcmctree.hessian * File with gradient and hessian matrix
checkpoint = 1 * 0: nothing; 1 : save; 2: resume
ndata = 1 * number of partitions
seqtype = 0 * 0 : nucleotides; 1: codons; 2: AAs (not required if the approximate likelihood method is used)
usedata = 2 * 0: sampling from priors with no data; 1: exact slow likelihood; 2: approximate likelihood
clock = 2 * 1: global clock with equal rates; 2: independent rates; 3: correlated rates
RootAge = <1.0 * safe constraint on root age, used if no fossil for root in the rooted tree file.
BDparas = 1 1 0.5 * birth-rate, death rate, sampling priors for sampling times
finetune = 1: 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.01 .5 * auto (0 or 1) : times, musigma2, rates, mixing, paras, FossilErr
print = 1 * 1: normal output; 2: verbose output
*** These parameters are used for multi-loci partitioned data (ndata > 1), see dos Reis et al.(2013)
rgene_gamma = 2 2 * alpha and beta parameter of Dirichlet-gamma prior for mean rate across loci for clock=2 or 3
sigma2_gamma = 1 10 * alpha and beta parameter of Dirichlet-gamma prior for rate variance across loci for clock=2 or 3
*** These parameters control the MCMC run
burnin = 20000
sampfreq = 200
nsample = 50000
*** Note: Total number of MCMC iterations will be burnin + (sampfreq * nsample)
*** The following parameters only needed to run MCMCtree with exact likelihood (usedata = 1)
*** no need to change anything for approximate likelihood (usedata = 2)
model = 0 * 0:JC69, 1:K80, 2:F81, 3:F84, 4:HKY85
alpha = 0 * 0: No rate heterogeneity across sites; otherwise: fixed alpha parameter of the Gamma distribution
ncatG = 0 * Number of rate categories for the discrete Gamma distribution
cleandata = 0 * remove sites with ambiguity data (1:yes, 0:no)?
kappa_gamma = 6 2 * gamma prior for kappa of the HKY model
alpha_gamma = 1 1 * alpha and beta parameter of Gamma distribution for heterogeneous rates across sites
Note that, if you generate the hessain file from IQ-TREE, it is necessary to use the rooted tree file generated by IQ-TREE to be used in MCMCtree. The ckpfile and hessianfile options are new and only work with our modified PAML code. If you use another MCMCtree version/release, you can simply remove those options from control file and rename the hessian file to in.BV to run MCMCtree without any errors.
Least Square Dating (LSD2)
Since IQ-TREE 2.0.3, we integrate the least square dating (LSD2) method to build a time tree when you have date information for tips or ancestral nodes. So if you use this feature please cite:
Thu-Hien To, Matthieu Jung, Samantha Lycett, Olivier Gascuel (2016) Fast dating using least-squares criteria and algorithms. Syst. Biol. 65:82-97. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syv068
We will now walk through examples but the full options are:
TIME TREE RECONSTRUCTION:
--date FILE Dates of tips or ancestral nodes
--date TAXNAME Extract dates from taxon names after last '|'
--date-tip STRING Tip dates as a real number or YYYY-MM-DD
--date-root STRING Root date as a real number or YYYY-MM-DD
--date-ci NUM Number of replicates to compute confidence interval
--clock-sd NUM Std-dev for lognormal relaxed clock (default: 0.2)
--date-outlier NUM Z-score cutoff to exclude outlier nodes (e.g. 3)
--date-options ".." Extra options passing directly to LSD2
DISCLAIMER: Please download version 2.0.6 with new options like
--date-ci.This feature is new and might still have bugs. So suggestions and bug reports are much welcome.
Inferring time tree with tip dates
This is a common scenario e.g. in virus datasets where you have sampling time for many sequences. You need first to prepare a date file, which comprises several lines, each with a taxon name (from your sequence alignment) and its date separated by spaces, tabs, or blanks. Note that it is not required to have dates for all tips. For example, this date file is part of the new corona virus dataset:
hCoV-19/Wuhan-Hu-1 2019-12-31
hCoV-19/China/WF0028 2020-02
hCoV-19/USA/WA-S88 2020-03-01
hCoV-19/USA/CA-CDPH-UC1 2020
hCoV-19/Italy/SPL1 2020-01-29
hCoV-19/Spain/Valencia5 2020-02-27
hCoV-19/Australia/QLD01 2020-01-28
hCoV-19/Vietnam/CM295 2020-03-06
hCoV-19/bat/Yunnan 2013-07-24
hCoV-19/pangolin/Guangdong 2019-02-01:2019-12-31
The date information here can be uncertain. For example, hCoV-19/China/WF0028 was sampled in Feb 2020, hCoV-19/USA/CA-CDPH-UC1 was sampled in 2020, and hCoV-19/pangolin/Guangdong was sample between 1st Feb 2019 and 31st Dec 2019. For such data range you can use “NA” to mean that the lower or upper bound is missing, e.g.:
TaxonA 2018-02-01:NA
TaxonB NA:2018-03-31
which means that TaxonA was sampled after 1st Feb 2018 and TaxonB was sampled before 31st Mar 2018.
Now run IQ-TREE with:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE
where ALN_FILE is the sequence alignment and DATE_FILE is the date file. This single command line will perform three steps: (1) find the best-fit model using ModelFinder, (2) find the maximum likelihood (ML) tree with branch lengths in number of substitutions per site, and (3) rescale the branch lengths of the ML tree to build a time tree with dated ancestral node. As output IQ-TREE will additional print three files:
ALN_FILE.timetree.lsd: The report of LSD.ALN_FILE.timetree.nex: Time tree file in NEXUS format, that can be viewed nicely in FigTree (Click on “Node Labels” on the left tab and choose “Display” as “date” in FigTree, see figure below).ALN_FILE.timetree.nwk: Time tree file in NEWICK format.
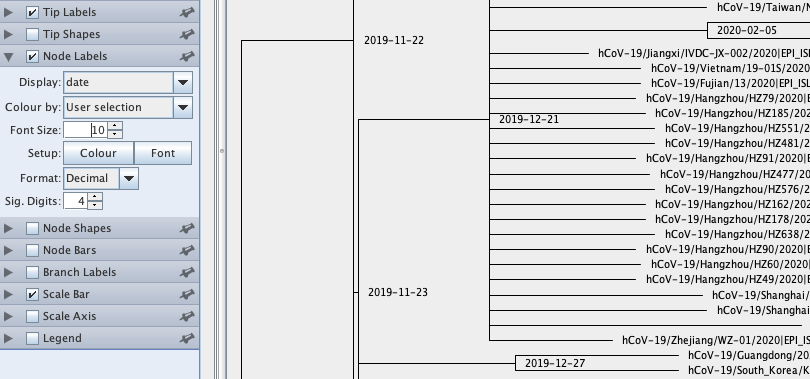
This command will automatically detect the best root position (according to LSD criterion). However, if the root is incorrectly inferred, it may produce wrong dates. Therefore, it is advisable to provide outgroup taxa if possible. In this example, we have this information, so you can use -o option:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE -o "hCoV-19/bat/Yunnan,hCoV-19/pangolin/Guangdong"
to instruct IQ-TREE that the root is on the branch separating bat and pangolin sequences from the rest.
Alternatively you can also append the dates into the sequence names of the alignment file using the | separator, such as (assuming a FASTA file here):
>hCoV-19/Wuhan-Hu-1|2019-12-31
......
>hCoV-19/China/WF0028|2020-02
......
>hCoV-19/USA/WA-S88|2020-03-01
......
>hCoV-19/USA/CA-CDPH-UC1|2020
......
>hCoV-19/Italy/SPL1|2020-01-29
......
>hCoV-19/Spain/Valencia5|2020-02-27
......
>hCoV-19/Australia/QLD01|2020-01-28
......
>hCoV-19/Vietnam/CM295|2020-03-06
......
>hCoV-19/bat/Yunnan|2013-07-24
......
>hCoV-19/pangolin/Guangdong|2019
......
Then run IQ-TREE:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date TAXNAME -o "hCoV-19/bat/Yunnan,hCoV-19/pangolin/Guangdong"
The special keyword TAXNAME for the --date option instructs IQ-TREE to automatically extract the dates from the taxon names.
Calibrating tree using ancestral dates
Another scenario is that we have sequences from present day and want to calibrate the dates of the ancestral nodes. This will only work if you have fossil date record of at least one ancestral node in the tree. Then you again need to prepare a date file which looks like:
taxon1,taxon2 -50
taxon3,taxon4,taxon5 -100
taxon6 -10
which, for example, mean that the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of taxon1 and taxon2 was 50 mya (million year ago) and the MRCA of taxon3, taxon4, taxon5 was 100 mya. Note that no empty space should be added to the comma-separated list of taxa, as empty space is used as a separator between taxon list and dates.
Now run IQ-TREE:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE --date-tip 0
This means that except for taxon6, all other taxa have the date of 0 for presence.
If you know the root date, then you can set it via --date-root option.
Dating an existing tree
If you already have a tree, you can use option -te TREE_FILE to ask IQ-TREE to load and fix this tree topology:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE -te TREE_FILE
This will work with the scenarios above, i.e., IQ-TREE will date the user-defined tree instead of the ML tree. To further speed up the process: If you know the model already, you set can it via -m option; or in a partitioned analysis, you can provide a partition file with specified models.
Obtaining confidence intervals
To infer the confidence interval of the estimated dates, use --date-ci option:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE --date-ci 100
which will resample branch lengths 100 times to infer the confidence intervals. Note that this is not bootstrap and the method is much faster but unpublished. Roughly speaking, it is based on a mixture of Poisson and lognormal distributions for a relaxed clock model. You can control the standard deviation of the lognormal distribution via --clock-sd option. The default is 0.2. If you set a higher value, the confidence interval will become wider.
Excluding outlier taxa/nodes
Long branches may cause biased date estimates. To detect and exclude outlier taxa or nodes prior to dating, use --date-outlier option:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE --date-outlier 3
that specifies a z-score threshold to detect outliers. The higher this value is, the more outliers will be removed from the resulting time tree.
Full list of LSD2 options
The main options in IQ-TREE provide easy access to the key LSD2 functions. If you would like more control of what LSD2 is doing, you can use the --date-options "..." command to pass any valid options to LSD2. For example, to control the way that LSD2 treats outliers, you can do this:
iqtree -s ALN_FILE --date DATE_FILE --date-options "-e 2"
A full list of the options for LSD2 can be obtained by downloading LSD2 and running lsd2 -h, the output of that command is provided here for your convenience.
Documentation
Assessing Phylogenetic Assumptions
Phylogenetic Dating
- Bayesian dating with MCMCtree
- IQ2MC workflow for time tree inference
- Estimating the gradients and the Hessian for MCMCtree dating
- Using partitions and Mixture models for approximate likelihood dating
- How to run MCMCtree
- Least Square Dating (LSD2)
- Inferring time tree with tip dates
- Calibrating tree using ancestral dates
- Dating an existing tree
- Obtaining confidence intervals
- Excluding outlier taxa/nodes
- Full list of LSD2 options
Simulating sequence alignments